Biggest solar storm on Earth in more than 20 years occurred last weekend, producing breathtaking auroras and posing concerns about the consequences of solar activity. The incident and its ramifications are explained simply here:
Just what happened?
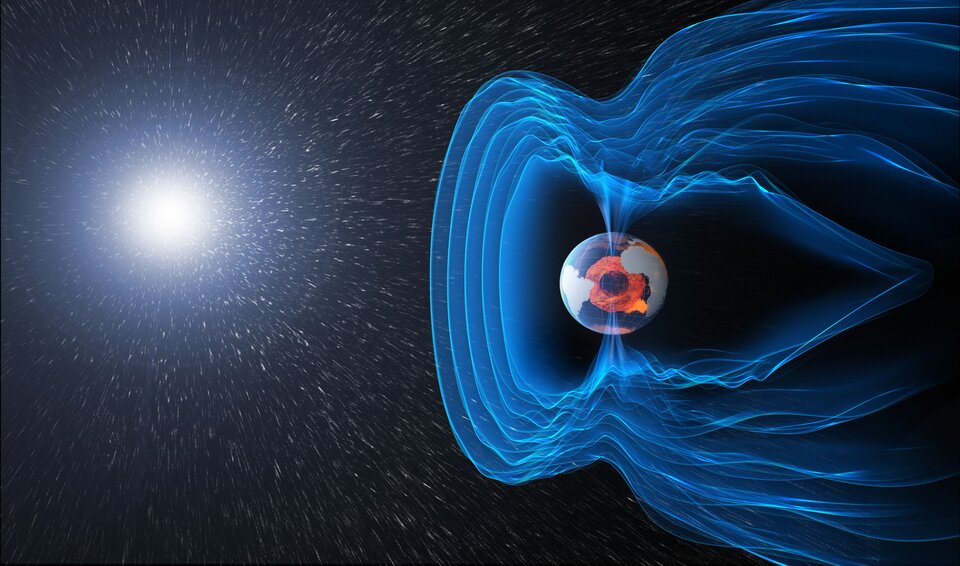
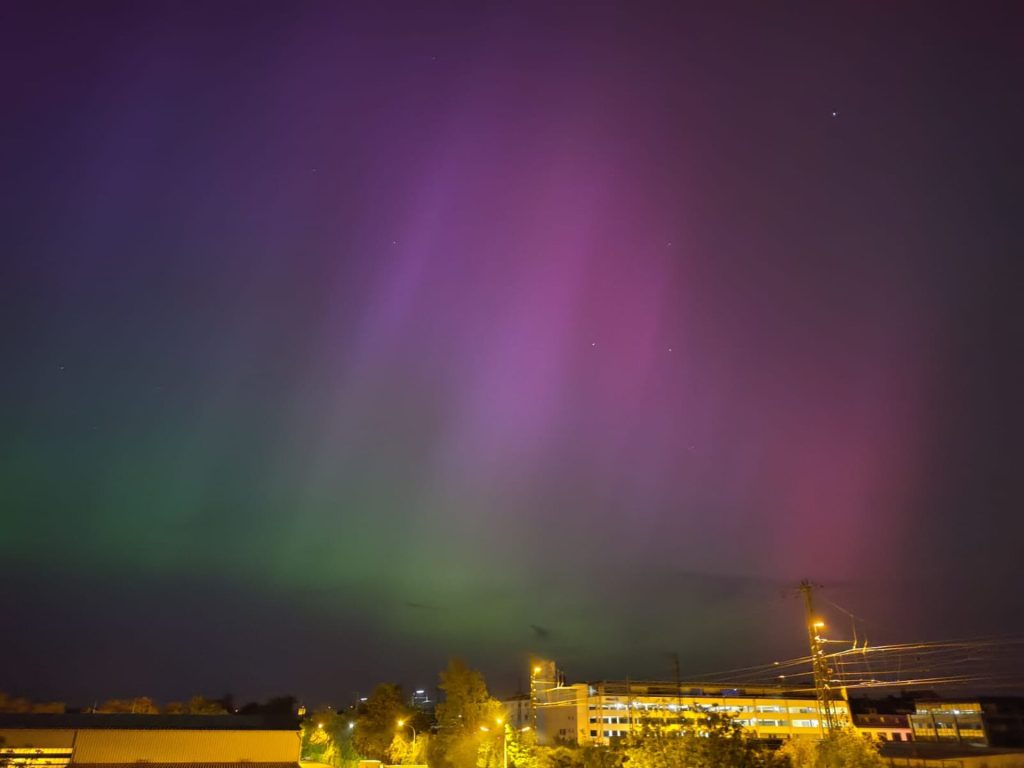
Multiple eruptions of a sizable active zone of the Sun facing Earth resulted in a powerful solar storm. Numerous big solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) during this storm carried magnetized plasma toward Earth. Normally shielding us, Earth’s magnetic field was greatly stretched this time, allowing charged particles to interact with our atmosphere and create auroras at lower latitudes than normal.
How Large Was This Storm?
A cycle of activity lasts eleven years on the Sun. Now we are getting close to the solar maximum, the highest point of this cycle when solar storms are most common. The Sun can snap its highly twisted magnetic field, releasing enormous amounts of energy and plasma.
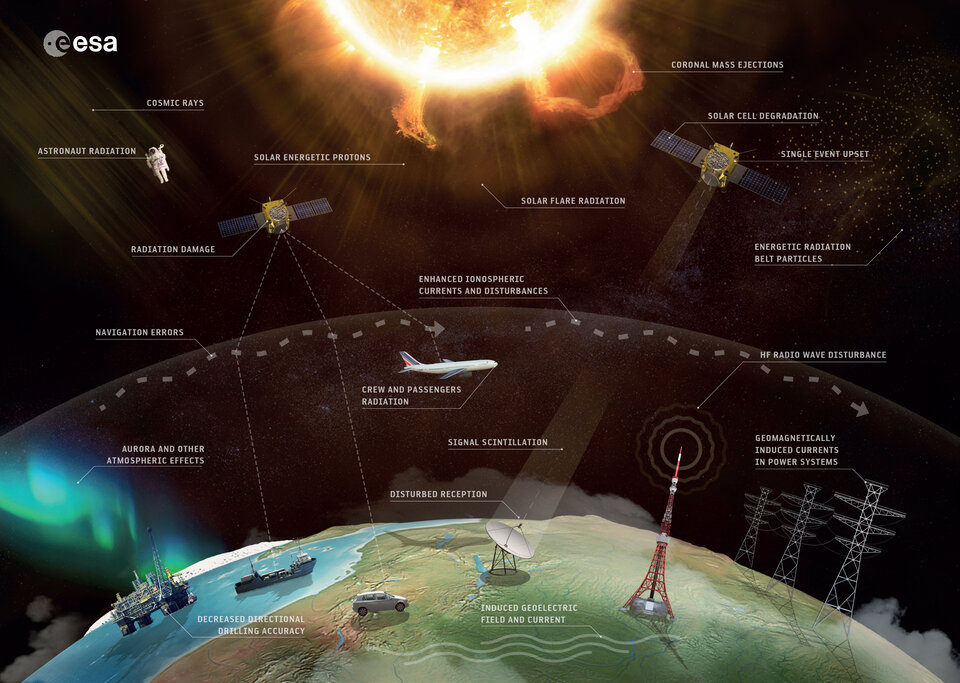
How Dangerous Are Solar Storms This Size?
The magnetic field and atmosphere of Earth make these storms not immediately hazardous to those living on its surface. Satellites, astronauts, and high-altitude aircraft may all be at danger from them, though. Radio communications, satellite operations, and power grids can all be hampered by space weather. The reduction of these hazards depends on prompt warnings.
Whence Came This Storm?
Though we can foresee the possibility of solar eruptions, it is difficult to predict their precise date and size. To issue warnings, the European Space Agency (ESA) and other agencies regularly track solar activity. Because solar flares move at the speed of light, there is little warning time. Slower moving CMEs give you a few days to get ready.
What Impact Did Earth Feel?
Multiple effects of the storm included:
Dayside radio transmissions on Earth were hampered by electromagnetic radiation.
Particles of high energy endangered spacecraft.
A wide variety of latitudes saw the auroras.
Reviewing the preparations made by different sectors, the effect on technology is still being evaluated.
How Were Missions of ESA Affected?
Radiation-resistant satellites operated by ESA escaped damage. But when space weather strikes, Earth’s atmosphere swells, which increases satellite drag and makes detecting space debris more difficult. At such times, low-Earth orbit satellites must make additional manoeuvres to prevent collisions.
And After That?
The latest storm’s causing active solar area has vanished from view, but new ones are starting to show. Future instances of space weather will be predicted and responded to via monitoring.

About Space Weather, What is ESA Doing?
To safeguard our technology and economy, the Space Weather Office of ESA tracks and forecasts space weather. Solar Orbiter and SOHO are two of the missions they utilize to investigate and comprehend the Sun. Launching in 2031, future missions such as Vigil will improve our capacity to forecast solar storms, offering early warnings and improved readiness.
Through knowledge of solar storms and enhancement of our reaction skills, we can lessen the effects of these amazing but maybe disrupting natural occurrences.